Oct 17th 2024
Hydroponic Grow Lights: Everything You Need to Know
Selecting the appropriate grow lights is very important when you’re growing plants in hydroponic system in order to provide them with the necessary light to flourish and yield a plentiful crop. Let us help you choose the finest hydroponic grow lights using the guidelines below.
How Do Grow Lights Work in a Hydroponic System?
The first thing that comes to anyone's mind is why grow lights are necessary when there is plenty of sunlight. Of course, we know that plants rely on the sun to provide the energy they need to grow and propagate. But how can you replace sunshine when producing vegetables indoors? A million-dollar question, with an answer: we substitute sunlight with a grow light. They essentially function the same way. In the past, high-intensity discharge light sources like ceramic metal halide (CMH) and high-pressure sodium (HPS) were used for this purpose. In recent years, advances in the pricing and manufacture of LED technology have enabled the emergence of a new generation of grow lights, making producing food in a hydroponic system considerably easier.

LED lights use electricity to create photons, or light particles, which the plants use for photosynthesis in the same manner as they would with photons from the sun. To create energy, plants use photons with a certain wavelength, or color as perceived by humans. Photosynthesis-friendly photon wavelength range is known as "photosynthetically active radiation," or PAR. The quantity of PAR a light produces per second, or its PPF (Photosynthetic Photon Flux), is what determines a grow light's output. This indicates how much of the light being generated will reach the plants you are cultivating, and is one of the most crucial metrics.
What are the Different Types of Lights Available?
Hydroponics allows for the use of a wide variety of lighting systems; the kind you choose will depend on the kind of plants you are growing and their developmental stage. Fluorescent, high-intensity discharge (HID), and light-emitting diode (LED) lights are a few of the most popular lighting types used in hydroponics:
- Fluorescent Lighting
- High-Intensity Discharge Lighting
- Light-Emitting Diode Lighting
Light Requirements for Hydroponic Plants
Plants in hydroponic systems require artificial light to grow and flourish because they are often housed inside. However, what precisely is included in a hydroponic lighting system? Growers need to take a few things into account when selecting hydroponic lighting.
Light Duration
The photoperiod is the length of time, during a particular 24-hour period, that a plant is exposed to light. Photoperiodism is the term used to describe how a plant reacts to the photoperiod. The development and health of the plant is highly dependent on this. You want to replicate the photoperiod of when your hydroponic plants would normally flourish outside. Think about the areas in which these plants are usually cultivated and the seasons in which they flourish.
As the plant gets bigger, you should also modify the photoperiod. As the crop matures, extend the photoperiod if it is a crop that is typically sown in the early spring. You should gradually decrease the photoperiod for plants that are seeded in the late summer.
Light Intensity
The intensity of a plant's daily light, in addition to its quantity, has a major impact on its development and well-being. According to TexasA&M's AgriLife Extension, "The production of plant food, stem length, leaf color, and flowering are all influenced by light intensity."
Similar to photoperiods, you should adjust light intensity based on the kind of plants you've selected. In reality, low-light plants grow just as well as high-light ones with less brightness. Nevertheless, it's usually preferable to err on the side of excessive brightness.
Light Spectrum
Another significant aspect of the light that plants receive is the color they have. The frequency of light waves, which is frequently expressed in wavelengths or nanometers, determines color. We are able to detect visible light between 400 nm (violet) and 780 nm (red). Wavelengths such as UVA (315–400 nm), UVB (280–315 nm), and infrared (700–1,000 nm) are outside of this range.
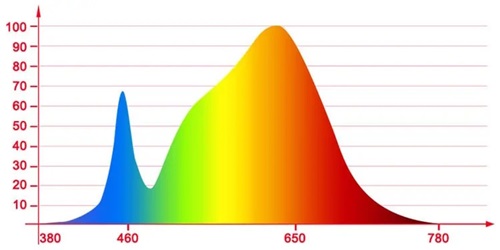
The impact of various illumination wavelengths on plant development will vary. Plants blossom at the lowest wavelengths, but yields can be increased by the highest wavelengths. The majority of indoor growers utilize many lights in various hues as a result of these variations.
How to Choose Wisely
Achieving a high-quality hydroponic garden starts with knowing how important lighting is and what to take into account while setting up your system. The most common error we've seen among beginner growers is selecting a light source that is too small or inadequate. Naturally, we want to go with something smaller and less expensive, but believe us when we say you will be disappointed. If you're still puzzled, there are grow systems with built-in grow lights that do all of the work for you. If you’re looking for high quality hydroponic system with grow lights then look no further than ALTO Garden. The GX Hydroponic Tower Garden with built in grow lights is designed to ensure that you get the most production out of your hydroponic system.
Final Thoughts
Hydroponic farming relies heavily on grow lights, as this page has discussed. Growers may optimize crop yields and improve nutrient absorption by specifying the light intensity, duration, location, and spectrum. It is significant to remember that various crops could have particular lighting needs, and producers should adjust their lighting plans accordingly. To guarantee the best outcomes, lighting conditions should also be constantly monitored and adjusted.




